Understanding What TESE Involves
Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) is a surgical procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles. It is typically recommended for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, a condition where no sperm is found in the ejaculate due to impaired sperm production. TESE offers a solution for couples struggling with severe male infertility and allows the use of retrieved sperm for assisted reproductive techniques such as ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection). This procedure is usually done when sperm cannot be obtained through other less invasive methods.
Who Benefits From TESE Treatment
TESE is a suitable option for men with genetic conditions, testicular failure, or those who have undergone cancer treatments affecting sperm production. It may also be used in cases where sperm is absent due to previous vasectomy or failed vasectomy reversal. The retrieved sperm, although limited in number, can still be viable for use in IVF procedures. TESE helps many couples who previously had no options for biological parenthood to move forward with fertility treatment using the male partner’s genetic material.
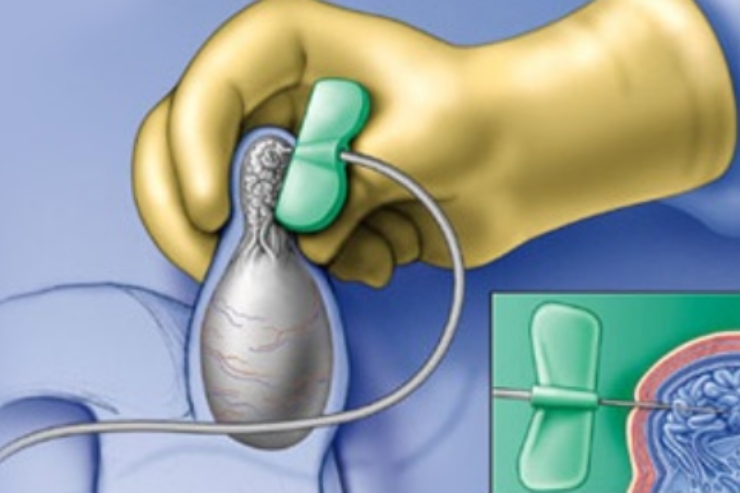
How TESE Procedure Is Done
TESE is typically performed under local or general anesthesia. A small incision is made in the scrotum to access the testicular tissue, from which small samples are taken. These tissue samples are examined in a laboratory to locate viable sperm. The procedure may take 30–60 minutes, and recovery is usually quick with minimal discomfort. The sperm collected can be used fresh or frozen for future fertility treatments. TESE is considered safe and effective when performed by skilled specialists, and it plays a key role in modern fertility care for male factor infertility.